

So all we have to do now is use the correct units, which would be grams per mole, or g/mol. First, we need to find the molar mass of each element in the compound: - Nitrogen (N): 14 g/mol - Hydrogen (H): 1 g/mol - Sulfur (S): 32 g/mol Now, lets find. It means when you have one mole of nitrogen, it is equivalent to about #14.01# grams of nitrogen, and it is also equivalent to about #6.02214 * 10^23# nitrogen atoms:ġ4.01 g N = 1 mol N atoms = #6.022 * 10^23# N atoms Numerically, this is the molar mass of nitrogen. Using a periodic table, we can find that nitrogen has an atomic mass of about #14.01# amu. This number, #6.02214 * 10^23#, is called Avogadro's number and is very useful when finding molar mass and converting between grams, moles, and particles. Numerically, it's the same as the element's atomic mass in units of amu (atomic mass units).Ī mole, or mol for short, is a quantity of any given thing that is equal to #6.02214 * 10^23# particles. Atomic weights of elements with atomic numbers 110-116 taken from this source.Molar mass is the quantity of an element in grams for every one mole of atoms of that element. IUPAC Standard Atomic Weights Revised (2005).Atomic weights of elements with atomic numbers from 1-109 taken from this source. Atomic Weights of the Elements 2001, Pure Appl.
#Atomic mass of n series

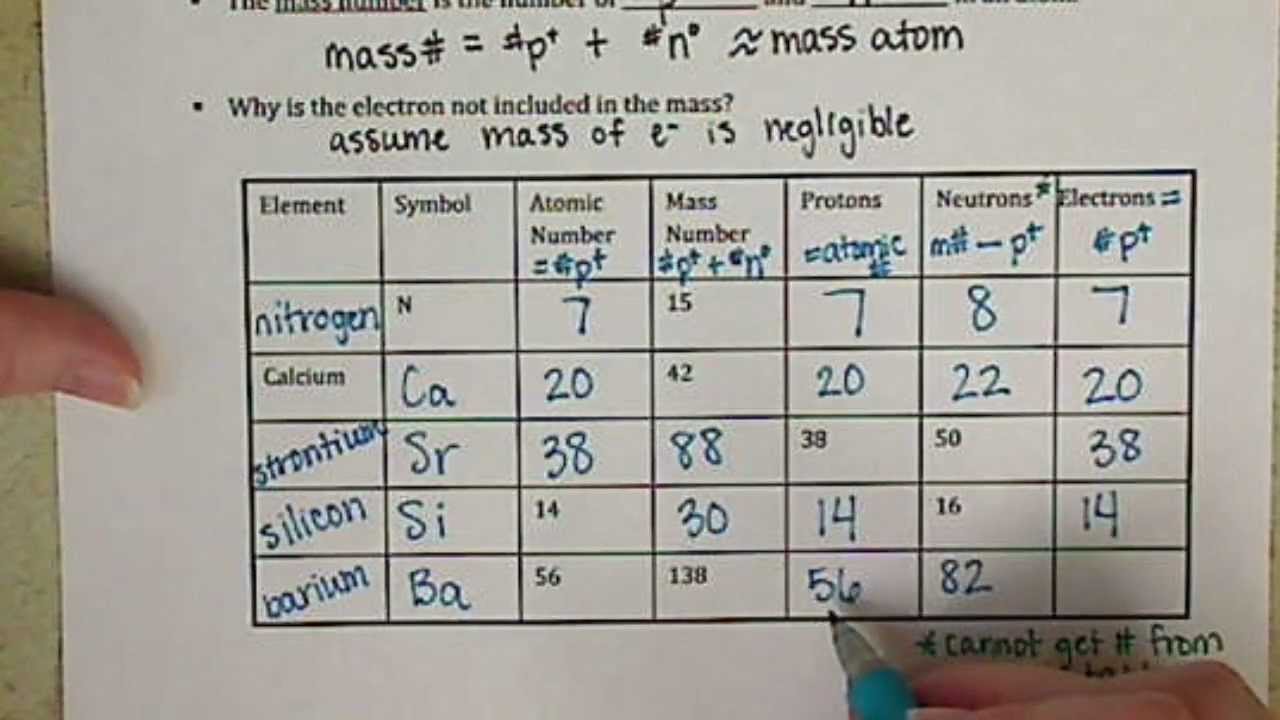

However, three elements, Thorium, Protactinium, and Uranium, have a characteristic terrestrial isotopic composition, and thus their atomic mass given. , indicates the mass number of the longest-lived isotope of the element. Note 1: The element does not have any stable nuclides, and a value in brackets, e.g.Chemical Series of the Periodic Table Alkali metalsĬhemical Series of the Periodic Table Alkali metalsĬhemical series of the periodic table notes: For artificial elements the nucleon count of the most stable isotope is listed as the atomic mass. Atoms of the element chromium ( Cr) have an atomic number of 24 and a mass number of 52. (3.4.1) Number of neutrons rounded mass number atomic number. The number in parenthesis gives the uncertainty in the "concise notation" defined in the IUPAC reference "whereby standard uncertainty is given in parenthesis next to the least significant digits to which it applies", e.g., 1.00794(7) stands for 1.00794 ± 0.00007. Knowing the mass number and the atomic number of an atom allows you to determine the number of neutrons present in that atom by subtraction. Each element's atomic number, name, element symbol, and group and period numbers on the periodic table are given.
#Atomic mass of n free
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia This is a list of chemical elements, sorted by atomic mass (or most stable isotope) and color coded according to type of element.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
